Chapter=2
Gauss' Theorem
*Electric Flux
The number of electric field lines passing perpendicular to the plane surface is called Electric Flux.
(3). Electric field due to an infinity plane sheet of charge.
(4). Electric field due to Two infinite parallel Sheets of charge
*. Gauss' Theorem
The net electric flux through a closed surface (3-D) is 1/ε0 times the net charge enclosed by the surface.
*Gauss' law is always applicable but not always useful.
1). The gaussion surface should be symmetric about 1 charge distribution.
2). The electric field must be symmetric(equal\constant\same) at all point of Gaussian surface.
3). The θ(Angle between and E &A) must be same at all point of the surface.
4). Gaussion surface must not pass through any point charge.
*. Application of Gauss law
(1). Electric field due to a point charge: introduction of Coulomb Law from Gauss'Theorem.
(2). Electric field due to a infinite line of charge.
1) Outside (r>R)
_________________________________
















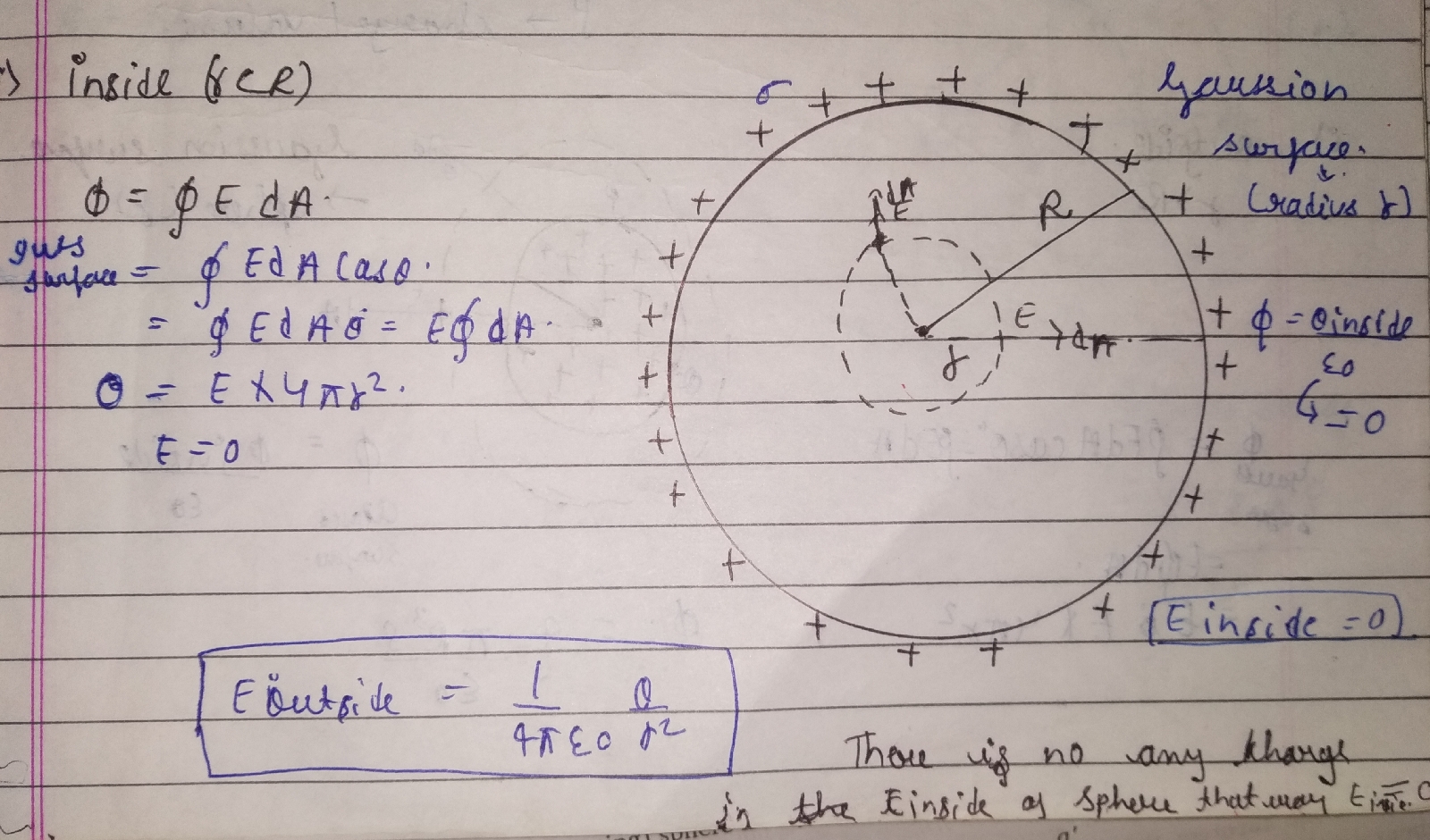





![Physics Electrostatics chapter 1[electric charges and fields]{part 1}](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhfv9lUqSNKCtEAW-shoepDa1dHgFIVFWyRmFHBztgnE7BP-LksUQxppfgH6VpKDS_FCCYM5ez4uRB-KqaRVFez49ScE_ZUfRUPy5JS387XJglidO5j1TJPXLrTZgIDNvg-xfd7X6qq6A/w680/1593057662528945-0.png)


0 Comments